How to measure, understand, and influence buying behavior
Buying behavior is the way people shop for your product, from product discovery to purchase and, in some cases, repurchase. It encompasses the practical, personal, and social factors that influence a buyer’s purchase decision, including both rational and irrational decision drivers.
Buying behavior includes data points like time of purchase, length of purchase, method of purchase, consumer preference for certain products, purchase frequency, and other similar metrics that measure how people shop for your products. These metrics can be grouped into different types of buying behavior that describe how buyers engage with a purchase decision.
Why is buying behavior important?
The type of buying behavior, along with the practical, personal, and social factors that influence it, gives you insight into the real reasons people buy your products. These insights help you create marketing messages that accelerate your customers’ purchase decisions.
With a strong understanding of buying behavior, you can:
- Adjust your marketing messages to suit the fluid purchasing behavior of your buyers.
- Create targeted messaging that resonates with specific types of buyers.
- Time your messaging so it reaches buyers when they typically purchase your product—like on holidays, on weekends, or when they use up an existing product.
- Help overwhelmed buyers work through dissonance reducing buying behavior with reassuring messaging that simplifies the purchase decision.
What influences buying behavior
Rational considerations like price, quality, and convenience all influence buying behavior, as do irrational considerations like feelings and desires. Most purchase decisions include a combination of unique mental, emotional, and behavioral factors.
- Mental (or “cognitive”) factors include rational considerations like product value
- Emotional (or “affective”) factors include irrational considerations like personal beliefs
- Behavioral (or “conative”) factors include buying patterns like brand loyalty
Every buyer has a “black box” of mental, emotional, and behavioral factors that affect their buying behavior. The contents of this box depends on the lifestyle, consumption habits, personal values, relationships, brand loyalties, personality, and demographics of the buyer.
People ultimately choose to buy products based on their immediate needs and personal preferences, as well as their exposure to marketing messages and social influences. Effective marketing messages and recommendations resonate with buyers in a mental or emotional way.
Some of the factors that influence buying behavior—like social trends, for example—are dynamic. As peer groups, societal norms, and cultural fads change, so does buying behavior. Agile market research helps your businesses stay on top of shifting consumer behavior.
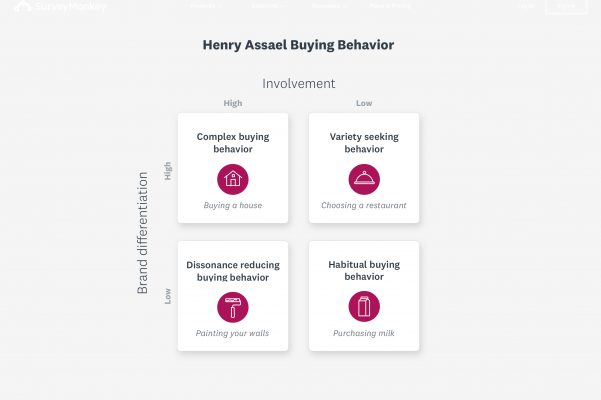
Types of buying behavior
There are four main types of buying behavior: complex behavior, dissonance reducing behavior, habitual behavior, and variety seeking behavior. Most purchases fall into one of these four categories, but buyers can react differently to the same purchases.
People usually engage in complex buying behavior when they make a big purchase—like a new car or house. People are highly involved in these purchase decisions and will research all their options thoroughly before settling on one. This type of buying behavior comes out when a purchase will impact a person’s life significantly, or the purchase comes with significant risks.
Someone who buys the same product over and over is exhibiting habitual buying behavior and high product loyalty. For example, a consumer might habitually purchase the same brand of sunscreen or milk every time they go shopping. They’ll make these purchases without spending time researching alternatives—because they don’t feel the need to stray from their go-to brand.
The opposite of habitual buying behavior is variety seeking buying behavior. People seek variety because they’re still searching for a favorite product or because they’re looking for novelty in their purchases. Someone might express variety seeking behavior when they frequently try different restaurants.
When people are afraid of making the wrong purchase decision, they express dissonance reducing buying behavior. This type of buying behavior is often linked to a fear of experiencing buyer’s remorse, which is usually based on a past experience with it. One example of dissonance reducing buying behavior coming into play is a consumer who spends a lot of time comparing different paint colors but significantly less time comparing paint brands.
Types of buyers
Most buyers express fluid buying behavior that changes from purchase to purchase. People typically make some habitual purchases—like drinking the same coffee every morning—but thoroughly research other more significant purchases. Many people will try new products like a unique variety of chips on impulse, but are hesitant to commit to bigger unknown purchases.
The best indication of which type of buying behavior people will express in a specific situation or for a certain product is the amount of risk involved in the purchase. Because more expensive products are more of a financial risk, people are usually most involved in their priciest purchases.
If a purchase decision will affect multiple people, buyers exhibit more complex buying behavior that involves input from more participants. When a family purchases a new home, for example, the mental, emotional, and behavioral considerations of each family member are weighed and considered. When someone purchases property alone, the purchase decision depends less on social influence.
Demographics like age and income also affect buying behavior. For example, teenagers usually make less significant purchases than adults, which might make them more likely to engage in variety seeking buying behavior. People in secure financial situations might also be less likely to express dissonance reducing buying behavior, since their personal financial risks are lower.
While buying behavior is fluid, some buyers are more likely to engage in certain types of buying behavior based on their demographics or defining factors like whether they make purchases online or in store. Buyer personas connect types of consumers with types of buying behavior.
How to measure buying behavior
A customer behavior analysis is a type of consumer research that gathers both quantitative and qualitative data points—i.e. statistical data as well as open-ended reflections on buying behavior—from respondents. This type of customer analysis identifies buyer personas and tracks the buying behavior of each persona at different stages in the customer journey.
If your business already has strong customer analytics, you can identify buyer personas before you dive into behavioral research. RFM analysis and customer lifetime value calculations are both powerful ways to find valuable market segments in your customer data. You can also work backwards, filtering your research results by behavioral data to identify demographic correlations.
While there are many consumer research methods, including interviews and case studies, surveys are usually the easiest way to get data from your customers or target market. Market research surveys help you uncover the factors that influence consumer buying behaviors, while customer satisfaction surveys are a good way to gain insight into customer buying behavior.
Consumer buying behavior survey questions
Consumer behavior surveys tease out buying behavior—and the rational and irrational value drivers behind purchase decisions. They ask practical questions like “How many other people in your household use this product category?” as well as reflective questions like “Do you typically make decisions about which brand you’ll buy beforehand or at the time of purchase?”
Examples of how to use buying behavior data
When you understand how people behave when they shop for your product, you know how to interact with buyers in the crucial period between product discovery and purchase.
If a purchase decision involves complex buying behavior, for example, you’ll probably want to focus your marketing efforts on nurturing (rather than just identifying) leads. Because complex purchase decisions often take time, it makes sense to pursue leads for a longer period rather than quickly moving on to the next lead if a buyer is slow to act.
If a purchase decision involves dissonance reducing buying behavior, reassuring leads will probably be your top priority. If your purchase seems risky to consumers, they may require some kind of “insurance,” like a free trial or a money back guarantee, to feel comfortable making a purchase. You’ll want to focus your efforts on building trust with potential customers.
If a purchase decision involves habitual buying behavior, brand loyalty is very important. Your business may want to focus on nurturing brand loyalty with existing customers if your research shows that your most valuable market segments express this type of buying behavior.
If a purchase decision involves variety seeking behavior, it’s extra important to differentiate your product and stand out from the competition. Buyers who express this type of behavior often reward businesses that take more experimental approaches to product design and marketing.
探索更多資源

品牌行銷經理
品牌行銷經理可利用此工具組來瞭解目標受眾、推動品牌成長並增進投資報酬率。

查看 SurveyMonkey 消費性產品與服務解決方案
消費性產品與服務產業 (包括 CPG、旅遊及餐旅) 都依賴 SurveyMonkey 的深入解析來決定未來的發展。

探索 SurveyMonkey 零售解決方案
瞭解 SurveyMonkey 如何幫助零售公司應對千變萬化的市場趨勢、開發讓客戶滿意的產品,並創造能吸引廣大粉絲的品牌。

查看 SurveyMonkey 專業服務公司解決方案
查看專業服務組織如何使用 SurveyMonkey 獲得客戶和市場深入解析。